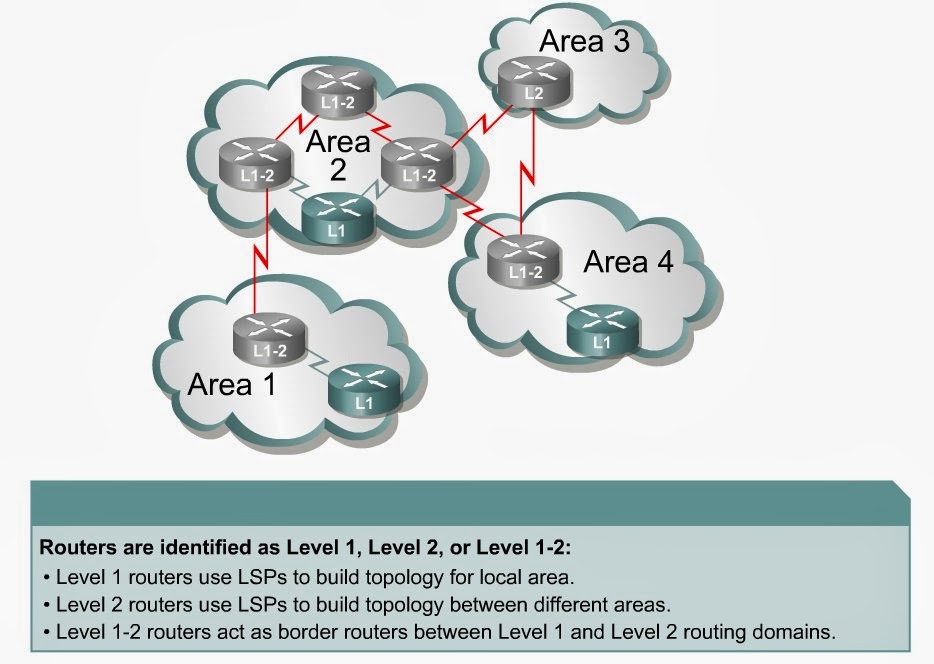
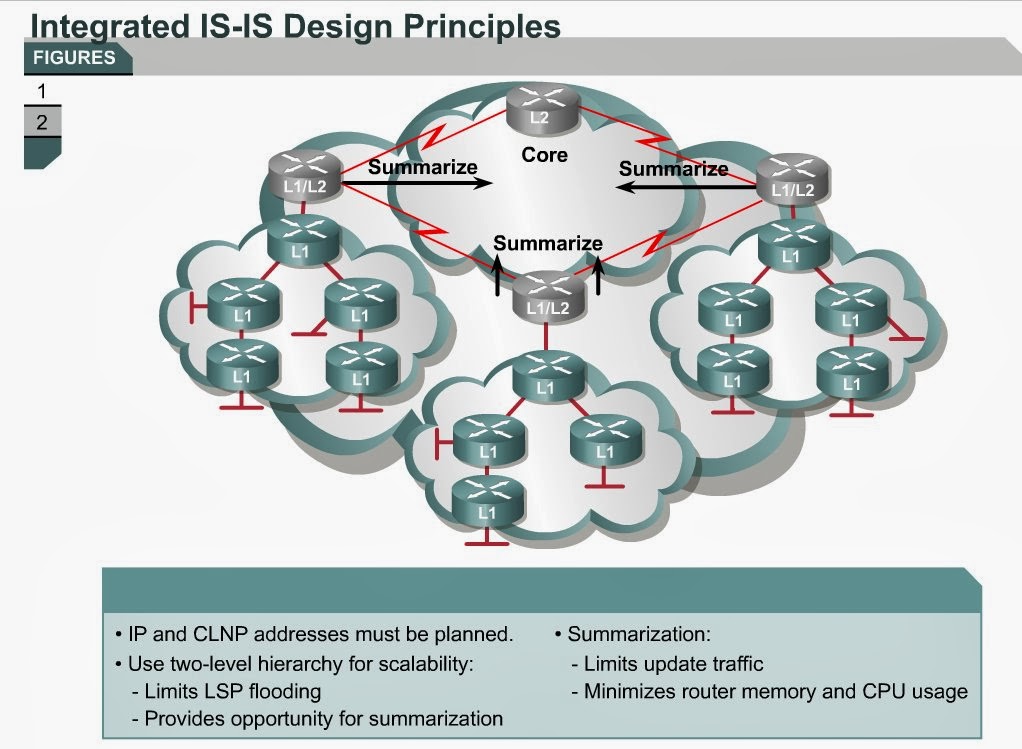
Терминология протокола IS-IS
- IS (Intermediate System) — маршрутизаторы.
- ES (End System) — хосты.
- CLNS (Connectionless Network Service) — протокол 3го уровня в стеке OSI, для передачи данных без установления соединения.
- LSP (Link-state Packet) - пакет состояния канала (аналог LSA в OSPF)
- CSNP (Complete Sequence Number PDU) - список всех состояний каналов (LSP) в базе данных состояний маршрутизатора (аналог пакета DD в OSPF). CSNP содержит LSP идентификатор, время жизни (lifetime), порядковый номер и контрольную сумму для каждой записи в базе данных.
- PSNP (Partial Sequence Number PDU) - запрос IS-IS маршрутизатора посылаемый для получения определенной LSP информации из базы данных соседнего маршрутизатора (аналог LSR в OSPF). Используется для: подтверждения получения одного из пакетов LSP (на участке сети point-to-point); запроса передачи уже существующего или отсутствующего в базе данных маршрутизатора LSP (на участках сети point-to-point или broadcast).
- DIS (Designated Intermediate System) - назначенная промежуточная система, используется для лавинной рассылки пакетов LSP от имени всех других маршрутизаторов данного сегмента
Адресация
Network Service Access Point (NSAP) addresses are subdivided into two parts:
Initial Domain Part (IDP) and Domain Specific Part (DSP).
AFI- Authority and Format Identifier (1-byte). Обычно используется 49 для приватных зон, аналогично как в IP приватные диапазоны.
IDI- Initial Domain Identifier (variable length). Identifies a subdomain under the AFI.
For instance, 47.0005 is assigned to civilian departments of the U.S. government, and 47.0006 is assigned to the U.S. Department of Defense.
HO-DSP - High-Order of DSP, subdivides the domain into areas. It is basically the OSI equivalent of a subnet in IP.
По сути это аналог IP-адреса.
System ID - identifies an individual OSI device. In OSI, a device has an address just as it does in DECnet; while in IP, each interface has an address.
По сути аналог MAC.
NSEL identifies a process on the device and corresponds roughly to a port or socket in IP. The NSEL is not used in routing decisions. Set in 00 to routers.
For example, you might assign 49.0001.0000.0c12.3456.00, which represents the following:
- AFI of 49
- Area ID of 0001
- System ID of 0000.0c12.3456, the MAC address of a LAN interface
- NSEL of 0
Роутинг
Значит, поясняю:
От X до Y он пойдёт вполне понятно почему так.
От Y до X он пойдёт через зону 4 потому что будет такая цепочка:
1) L1 роутер видит адрес назначения AREA 1, он не совпадает с адресом AREA 2, значит он будет отправлять пакет роутеру L1-2 для доставки дальше.
2) Встаёт логичный вопрос, а какому из двух роутеров L1-2 отправить пакет. Решение принимается по наименьшей цене доставки -- стоимость пути = 10.
Router Y routes return packets to router X via its nearest Level 1–2 router.
3) Роутер L1-2 просматривает адрес назначения, видит несовпадение area, оценивает расстояние до ближайшей area. Ближайшая area это area 4. Пакет уходит в area 4.
Как ни странна такая логика, но это не OSPF, решение принимает по самой низкой цене до ближайшего.
PDU
IS-IS defines four categories of PDUs:
- Hello (ESH, Intermediate System Hello [ISH], IS-IS Hello [IIH]): Establishes and maintains adjacencies. Once the neighbors have been discovered and have become adjacencies, the hello PDUs act as keepalives to maintain the adjacencies and to inform the neighbors of any changes in the topology.
- LSP: Distributes link-state information.
- Sequence
Number: Informs other routers of LSPs that may be outdated or
missing from their own database to ensure that all routers have the
same information and are synchronized (similar to an OSPF database
description packet).
There are two types of sequence number PDUs:- Complete sequence number (CSNP): Describes the complete list of all LSPs in the LSDB of a router
- Partial sequence number (PSNP): Requests and acknowledges missing pieces of link-state information
Пакет Link-State PDU (LSP) содержит информацию о маршрутизаторах в сети и о связях между их интерфейсами. Метрика и информация о IS-IS соседе также включена. Пакет имеет размер более 19 байт со следующей структурой:
- Length (2 байт) - общая длинна пакета LSP в байтах.
- Remaining Lifetime (2 байт) - это поле устанавливает время жизни LSP в течении которого каждый маршрутизатор считает этот LSP актуальным.
- LSP ID (8 байт) - это поле однозначно определяет LSP по всей сети. Значение представляет собой комбинацию System ID (6 байт), circuit ID (1 байт), номер LSP.
- Sequence Number (4 байт) - это поле указывает номер текущей версии LSP. Первоначальное число 0x01 увеличивается на единицу каждый раз, когда исходный маршрутизатор обновляет LSP.
- Checksum (2 байт) - это поле содержит контрольную сумму полей PDU.
- Attributes (1 байт) - это поле содержит информации о состоянии текущего маршрутизатора. Позиции битов поля означиют:
- Bit 7 - раздел
- Bit 6 - бит ошибки метрики
- Bit 5 - бит счет метрики
- Bit 4 - бит задержки метрики
- Bit 3 - бит для метрики по умолчанию. Используется L2 маршрутизатором для анонсирования подключения к L1 области.
- Bit 2 - бит перегрузки. Предупреждает другие IS-IS маршрутизаторы не использовать информацию, передаваемую в этом LSP.
- Bits 0 and 1 - бит определяет роль маршрутизатора. L1 маршрутизатор устанавливает значение 0x01. Маршрутизатор L1/L2 и L2 устанавливает значение 0x03.
- TLVs (размер не определен) - это поле содержит краткую информацию базы данных с локального маршрутизатора.
Типы TLV (type/length/value)
- TLV1 - Area address.
- TLV2 - IS reachability.
- TLV6 - IS neighbors.
- TLV8 - Padding TLV.
- TLV10 - Authentication.
- TLV22 - Extented IS reachability.
- TLV128 - IP internal reachability.
- TLV129 - Protocols supported.
- TLV130 - IP external reachability.
- TLV132 - IP interface addresses.
- TLV134 - TE IP router ID.
- TLV135 - Extended IP reachability.
- TLV137 - Dynamic hostname resolution.
- TLV222 - Multiple topology IS reachability.
- TLV229 - Multiple topologies supported.
- TLV232 - IPv6 interface address.
- TLV235 - Multiple topology IP reachability.
- TLV236 - IPv6 reachability.
- TLV237 - Multiple topology Reachable IPv6 TLV.
Type of network
Broadcast mode
Dijkstra’s algorithm requires a virtual router (a pseudonode), represented by the Designated Intermediate System (DIS), to build a directed graph for broadcast media. Criteria for DIS selection are, first, highest priority (the priority value is configurable) and, second, highest SNPA (on LANs, the SNPA is the MAC address).
LSP L1 L2
LSP Flooding Rules
- CLNS (Connectionless Network Service) — протокол 3го уровня в стеке OSI, для передачи данных без установления соединения.
- LSP (Link-state Packet) - пакет состояния канала (аналог LSA в OSPF)
- CSNP (Complete Sequence Number PDU) - список всех состояний каналов (LSP) в базе данных состояний маршрутизатора (аналог пакета DD в OSPF). CSNP содержит LSP идентификатор, время жизни (lifetime), порядковый номер и контрольную сумму для каждой записи в базе данных.
- PSNP (Partial Sequence Number PDU) - запрос IS-IS маршрутизатора посылаемый для получения определенной LSP информации из базы данных соседнего маршрутизатора (аналог LSR в OSPF). Используется для: подтверждения получения одного из пакетов LSP (на участке сети point-to-point); запроса передачи уже существующего или отсутствующего в базе данных маршрутизатора LSP (на участках сети point-to-point или broadcast).
- DIS (Designated Intermediate System) - назначенная промежуточная система, используется для лавинной рассылки пакетов LSP от имени всех других маршрутизаторов данного сегмента
LSDB Synchrization
Sequence number PDUs (SNPs) are used to acknowledge the receipt of LSPs and to maintain LSDB synchronization. There are two types of SNPs:
- CSNP
- PSNP
CSNPs and PSNPs share the same format. Each carries summarized LSP information. The main difference is that CSNPs contain summaries of all LSPs in the LSDB, while PSNPs contain only a subset of LSP entries.
Separate CSNPs and PSNPs are used for Level 1 and Level 2 adjacencies.
Adjacent IS-IS routers exchange CSNPs to compare their LSDB. In broadcast subnetworks, only the DIS transmits CSNPs. All adjacent neighbors compare the LSP summaries received in the CSNP with the contents of their local LSDBs to determine if their LSDBs are synchronized (in other words, if they have the same copies of LSPs as other routers for the appropriate levels and area of routing).
CSNPs are periodically multicast (every 10 seconds) by the DIS on a LAN to ensure LSDB accuracy.
If there are too many LSPs to include in one CSNP, the LSPs are sent in ranges. The CSNP header indicates the starting and ending LSP ID in the range. If all LSPs fit in the CSNP, the range is set to default values.
Adjacent IS-IS routers use PSNPs to acknowledge the receipt of LSPs and to request transmission of missing or newer LSPs.
On point-to-point networks, CSNPs are sent when the link comes up to synchronize the LSDBs.
Example LAN
On a LAN, the DIS sends CSNPs that list the LSPs that it has in its LSDB every 10 seconds. This update is sent as a multicast to all Level 1 or Level 2 IS-IS routers on the LAN.
In Figure, router R1 compares this list of LSPs with its topology table and realizes that it is missing one LSP. Therefore, it sends a PSNP to the DIS (router R2) to request the missing LSP.
The DIS reissues only that missing LSP (LSP 77), and R1 acknowledges it with a PSNP.
Example Point-to-point
- A link fails.
- Router R2 notices this failure and issues a new LSP noting the change.
- Router R1 receives the LSP, stores it in its topology table, and sends a PSNP back to R2 to acknowledge receipt of the LSP.
CLNS, NET ADDRESS, ROUTING
A NET address identifies a device (an intermediate system [IS] or end system [ES]) and not an interface. This is a critical difference between a NET address and an IP address. A device identifies other devices within its own area based on matching area addresses in their NET.
А еси по-русски и доходчиво: NET адрес характеризует адрес устройства целиком, а не один интерфейс, как IP адрес. Что вполне логично, поскольку в IS-IS устройство может принадлежать только одной зоне, а граница между зонами - это "между интерфейсами".
Configuration
2. Enable IS-IS on the router
3. Configure the NET
4. Enable integrated IS-IS
Example 1
Example 2
5. Changing IS-IS Router Level
6. Changing IS-IS Interface level
Example
7. Changing IS-IS metric
Пример смотри выше. В конфиге роутера R2.
8. IP Summarization
Global Example.
Troubleshooting, show and debug
R2# show ip protocols
R2# show ip route isis
A NET address identifies a device (an intermediate system [IS] or end system [ES]) and not an interface. This is a critical difference between a NET address and an IP address. A device identifies other devices within its own area based on matching area addresses in their NET.
А еси по-русски и доходчиво: NET адрес характеризует адрес устройства целиком, а не один интерфейс, как IP адрес. Что вполне логично, поскольку в IS-IS устройство может принадлежать только одной зоне, а граница между зонами - это "между интерфейсами".
Configuration
2. Enable IS-IS on the router
3. Configure the NET
4. Enable integrated IS-IS
Example 1
Example 2
5. Changing IS-IS Router Level
6. Changing IS-IS Interface level
Example
7. Changing IS-IS metric
Пример смотри выше. В конфиге роутера R2.
8. IP Summarization
Global Example.
Troubleshooting, show and debug
R2# show ip protocols
R2# show ip route isis